Building a Scalable Data Processing Pipeline: Integrating DynamoDB with Kinesis Data Stream, Firehose, Glue, and Athena on AWS
Amazon Web Services (AWS) provides a wide range of services that enable businesses to process, analyze, and store large volumes of data. DynamoDB, Kinesis Data Stream, Firehose, Glue, and Athena are some of the AWS services that can be used in combination to build a real-time data processing pipeline.
In this article, we will discuss how to integrate DynamoDB with Kinesis Data Stream, Firehose, Glue, and Athena to build a scalable, serverless, and cost-effective data processing pipeline. The article is inspired by this AWS Big Data Blog post and provides code with CDK.
Create the DynamoDB table and the Kinesis Data Stream
Amazon DynamoDB is a fully managed NoSQL database service that provides fast and predictable performance with seamless scalability. It is a serverless database that automatically scales up or down based on the workload, and provides low-latency access to data. DynamoDB stores data in tables, and each table consists of one or more items. An item is a collection of attributes that represent an individual record.
Amazon Kinesis Data Streams is a scalable and durable real-time data streaming service that enables you to ingest and process large volumes of data in real-time. Kinesis Data Stream is designed for applications that require real-time processing of streaming data such as IoT devices, mobile applications, social media feeds, log files, and clickstreams.
In the following code, we will create the DynamoDB table and the Kinesis Data Stream.
The Kinesis Data Stream will be connected to the DynamoDB via the kinesisStream property.
private createKinesisStream(): kinesis.Stream {
const kinesisStream = new kinesis.Stream(this, "Stream", {
streamName: "heartrate-kinesis",
shardCount: 1,
});
new dynamodb.Table(this, "Table", {
tableName: "heartrate-ddb",
partitionKey: {
name: "id",
type: dynamodb.AttributeType.STRING,
},
kinesisStream: kinesisStream,
removalPolicy: cdk.RemovalPolicy.DESTROY,
});
return kinesisStream;
}
Deliver the stream to a S3 bucket
In this section, we will deliver the Kinesis Data Stream to a S3 bucket, via Kinesis Firehose.
Amazon Kinesis Data Firehose is a fully managed service that ingests data streams and automatically delivers the data to destinations such as Amazon S3, Amazon Redshift, and Amazon Elasticsearch Service. Firehose is designed to be serverless and can scale up or down automatically based on the incoming data volume.
Since there is no L2 construct for Kinesis Firehose yet, we will rely on the L1 construct CfnDeliveryStream.
private createFirehoseToS3(kinesisStream: kinesis.Stream): s3.Bucket {
// Create a role for the Firehose service
const firehoseRole = new iam.Role(this, "FirehoseRole", {
assumedBy: new iam.ServicePrincipal("firehose.amazonaws.com"),
});
kinesisStream.grantRead(firehoseRole);
// Create the bucket to deliver the stream to
const bucket = new s3.Bucket(this, "Bucket", {
removalPolicy: cdk.RemovalPolicy.DESTROY,
autoDeleteObjects: true,
});
bucket.grantWrite(firehoseRole);
// Transform the stream data with EOL
const transformFirehose = new nodejs.NodejsFunction(
this,
"TransformFirehose",
{
entry: join(__dirname, "..", "functions", "firehose-json-eol.ts"),
handler: "handler",
logRetention: logs.RetentionDays.ONE_DAY,
}
);
transformFirehose.grantInvoke(firehoseRole);
const firehoseStreamToS3 = new firehose.CfnDeliveryStream(
this,
"FirehoseStreamToS3",
{
deliveryStreamName: "heartrate-firehose",
deliveryStreamType: "KinesisStreamAsSource",
kinesisStreamSourceConfiguration: {
roleArn: firehoseRole.roleArn,
kinesisStreamArn: kinesisStream.streamArn,
},
extendedS3DestinationConfiguration: {
bucketArn: bucket.bucketArn,
bufferingHints: {
sizeInMBs: 1,
intervalInSeconds: 60,
},
compressionFormat: "GZIP",
encryptionConfiguration: {
noEncryptionConfig: "NoEncryption",
},
prefix:
"data/year=!{timestamp:yyyy}/month=!{timestamp:MM}/day=!{timestamp:dd}/hour=!{timestamp:HH}/",
errorOutputPrefix: "errors/",
roleArn: firehoseRole.roleArn,
// IMPORTANT
processingConfiguration: {
enabled: true,
processors: [
{
type: "Lambda",
parameters: [
{
parameterName: "LambdaArn",
parameterValue: transformFirehose.functionArn,
},
{
parameterName: "RoleArn",
parameterValue: firehoseRole.roleArn,
},
],
},
],
},
},
}
);
// Ensures our role is created before we try to create a Kinesis Firehose
firehoseStreamToS3.node.addDependency(firehoseRole);
firehoseStreamToS3.node.addDependency(kinesisStream);
return bucket;
}
By default, Kinesis Data Firehose sends JSON records inline, which causes Athena to query only the first record in each S3 object. To overcome this, we use a Lambda function to transform records before sending them to Amazon S3 by adding an end of line (EOL) character.
Here is the code of the Lambda function:
import {
FirehoseTransformationHandler,
FirehoseTransformationResultRecord,
} from "aws-lambda";
export const handler: FirehoseTransformationHandler = async (event) => {
const output: FirehoseTransformationResultRecord[] = event.records.map(
(record) => {
let entry = Buffer.from(record.data, "base64").toString("utf8");
let result = entry + "\n";
const payload = Buffer.from(result, "utf8").toString("base64");
return {
...record,
data: payload,
result: "Ok",
};
}
);
return { records: output };
};
Create the Glue table
AWS Glue is a fully managed extract, transform, and load (ETL) service that makes it easy to move data between data stores. Glue can automatically discover and categorize data, convert data into formats suitable for analysis, and load data into various data stores. Glue is serverless and can scale up or down based on the size of the data.
While we could use a Glue Crawler to extract the data schema, since we know to exact format, we can create the Glue Table instead:
private createGlueTable(inputBucket: s3.Bucket): {
glueDatabase: glue.Database;
glueTable: glue.Table;
} {
const glueDatabase = new glue.Database(this, "GlueDatabase", {
databaseName: "heartrate-glue-db",
});
const glueTable = new glue.Table(this, "GlueTable", {
database: glueDatabase,
bucket: inputBucket,
tableName: "heartrate-glue-table",
dataFormat: glue.DataFormat.JSON,
columns: [
{
name: "dynamodb",
type: glue.Schema.struct([
{
name: "NewImage",
type: glue.Schema.struct([
{
name: "id",
type: glue.Schema.struct([
{
name: "S",
type: glue.Schema.STRING,
},
]),
},
{
name: "HeartRate",
type: glue.Schema.struct([
{
name: "S",
type: glue.Schema.INTEGER,
},
]),
},
{
name: "SensorID",
type: glue.Schema.struct([
{
name: "S",
type: glue.Schema.INTEGER,
},
]),
},
{
name: "ReportTime",
type: glue.Schema.struct([
{
name: "S",
type: glue.Schema.STRING,
},
]),
},
]),
},
]),
},
],
});
return { glueDatabase, glueTable };
}
Query the data with Athena
Amazon Athena is a serverless interactive query service that makes it easy to analyze data stored in Amazon S3 using SQL. Athena does not require any infrastructure to set up or manage, and it can handle structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data.
Let's create a workbench and named query:
private createAthena(glueDatabase: glue.Database, glueTable: glue.Table) {
const athenaOutputBucket = new s3.Bucket(this, "AthenaOutputBucket", {
autoDeleteObjects: true,
removalPolicy: cdk.RemovalPolicy.DESTROY,
});
const athenaRole = new iam.Role(this, "AthenaRole", {
assumedBy: new iam.ServicePrincipal("athena.amazonaws.com"),
});
athenaOutputBucket.grantReadWrite(athenaRole);
const ATHENA_OUTPUT_PREFIX = "athena-output";
const athenaWorkgroup = new athena.CfnWorkGroup(this, "AthenaWorkGroup", {
name: "heartrate-athena-workgroup",
workGroupConfiguration: {
resultConfiguration: {
outputLocation: `s3://${athenaOutputBucket.bucketName}/${ATHENA_OUTPUT_PREFIX}`,
},
},
});
const namedQuery = new athena.CfnNamedQuery(
this,
"query-current-ddb-state",
{
database: glueDatabase.databaseName,
queryString: `SELECT dynamodb.newimage.Id.S as ID,
dynamodb.newimage.HeartRate.S as HeartRate,
dynamodb.newimage.SensorID.S as SensorID,
dynamodb.newimage.ReportTime.S as ReportTime
FROM "${glueTable.tableName}"
WHERE dynamodb.newimage.HeartRate.S > 120
`,
name: "hight-heart-rate",
workGroup: athenaWorkgroup.name,
}
);
namedQuery.addDependency(athenaWorkgroup);
}
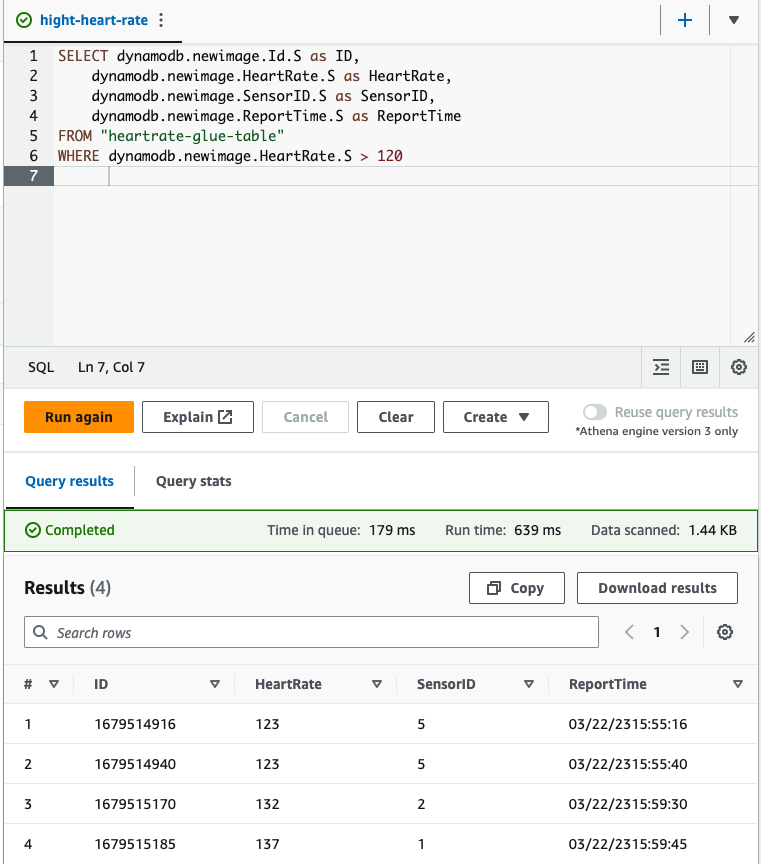
After adding data to the DynamoDB table, we can query the data with Athena:
Conclusion
In conclusion, integrating AWS services such as DynamoDB, Kinesis Data Stream, Firehose, Glue, and Athena can help businesses build a powerful and scalable data processing pipeline.
By ingesting real-time data from DynamoDB into Kinesis Data Stream, processing it using Firehose and Glue, and analyzing it using Athena, businesses can gain insights and make informed decisions in real-time.
This serverless and cost-effective solution provides the flexibility and scalability to handle large volumes of data, while also allowing businesses to focus on their core operations.
As the volume of data continues to grow, building a scalable data processing pipeline on AWS is essential for businesses to stay competitive in today's data-driven world.
Source code available on github
